For Intel, Xilinx and Achronix FPGAs
LOW Cost…HIGH Capacity…HIGH Performance FPGA attached memories
… Perfect for QDR Replacements and easy to design new systems
… Single Quazar device memory is 4-8 times a single QDR!
- Single device
- Provide high capacity
- Fully random access to all memory locations
- Low tRC
- Higher bandwidth
- Low power
- Simple FPGA SERDES interface
- Equal or better performance than a QDR at a system level
- Costs significantly less than the equivalent cost of a QDR configuration
QUAZAR FAMILY FEATURES/BENEFITS
- Today, systems are more complex. Bandwidth has increased tremendously. Gone is the reliance on single device’s technical specification.
- Data and information flow require a System Memory Strategy that involves the tradeoffs of DRAM, HBM, FPGA memory and the growing need for FPGA attached memories like Quazar.
- System architectures today must define the “system latency and bandwidth” and then choose the best memory combination.
- Access time
- Random-access flexibility
- Word width
- System latency
- Cost
- Etc.
With MoSys years of memory designs for systems, we designed our memory products to address performance at the system level to take the best of the QDR type devices and add significantly higher capacity and increase bandwidth.
TOPICS
QUAZAR DEVICE OVERVIEW
There are two Quazar QPR devices that attach directly with the FPGA and uses our Quad Partition Rate (QPR) technology to achieve QDR performance or better at a much lower cost!
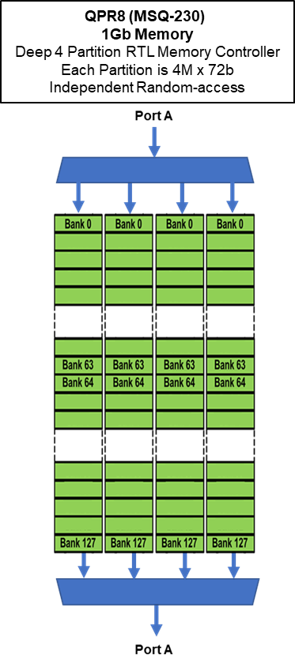
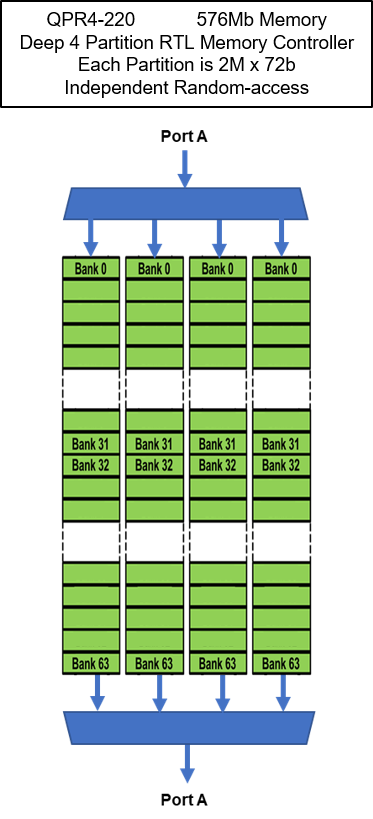
- QPR4 with 576Mb memory
- QPR8 with 1Gb memory
The flexibility of the QPR architecture allows the memory to operate in two user selected modes.
- DEEP Mode configures the access to the total memory capacity as 4 independent SRAMs
- WIDE Mode configures the access to the total memory capacity as 8 independent SRAMs
- Application bandwidth is determined by how many Partitions are accessed in one cycle.
- DEEP Mode – the Single clock access has a word width of up to 288b
- WIDE Mode – the Single clock access has a word width of up to 576b
The MoSys provides a FPGA Memory Controller RTL that controls the signals between the FPGA and the Quazar memory so you do not have to write RTL code which is either
- 16 SERDES lanes for DEEP Mode
- 32 SERDES lanes for WIDE Mode
The key to designing a low latency, high performance architecture requires system level considerations.
- Tradeoffs of Internal FPGA memory vs External memory
- FPGA internal memory
- External attached SRAM memory (like Quazar)
- HBM/DDR
Last key point…Local FPGA attached Quazar QPR memories can
- Lower latency and increase bandwidth
- Simplify the FPGA board design and signal integrity effort
- Free up many signal pins for other use!
- And as important, Frees up FPGA memory control cycles
DESIGNING CANNOT GET MUCH SIMPLER!
QUAZAR DEVICE – QPR4 and QPR8

Overview of Operating Modes
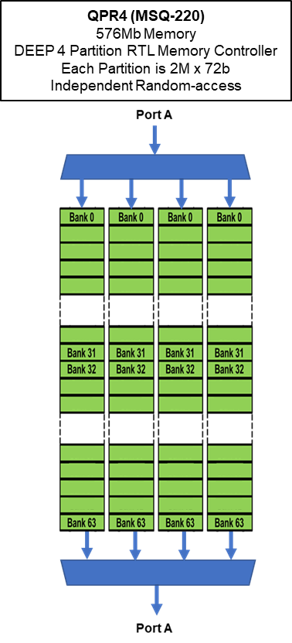
The QPR4 is shown here for Example
Two operating memory Modes: DEEP MODE and WIDE MODE
DEEP MODE OPERATION
MoSys RTL Memory Controller
- DEEP PARTITION QPR4
- Single Port A
- 1 SerDes Port of 8 lanes, 32 pins
- 4 QDR equivalent capacity
- 4 partitions (2M x 72) that are fully random-access memories Each partition is equivalent density to a QDR device
- Word with up to 288b
- Maximum bandwidth is 160 Gb/s (180 Gb/s full duplex)
Random-Access Bandwidth
Each Partition operates as an independent Random-Access SRAMs. All of the partition are accessed each tRC clock cycle.
Memory can be accessed at same address across all memories. High bandwidth with 288b word.
Or, each partition can access any location in its partition independently of the access locations of the other partitions.
In effect, 4 fully random-access independent SRAMs. Still achieving a 288b wide data path.
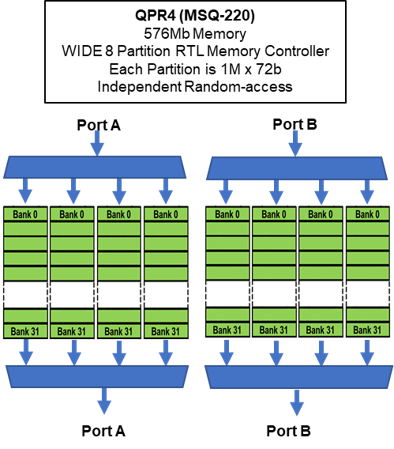
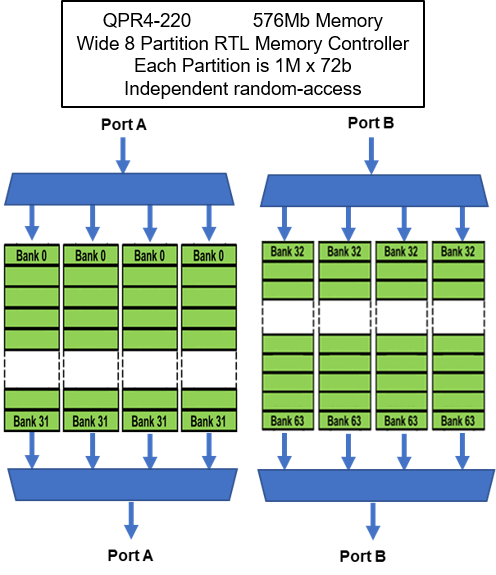
WIDE MODE OPERATION
MoSys RTL Memory Controller
- WIDE PARTITION QPR4
- 2 SerDes Ports
- Two Ports A and Port B
- 2 SerDes ports of 16 lanes, 64 pins
- 4 QDR equivalent capacity
- 8 partitions (1M x 72) that are fully random-access memories
- Word width up to 576b
- Maximum bandwidth is 320 Gb/s (160 Gb/s full duplex)
Random-Access Bandwidth
Each Partition operates as an independent Random-Access SRAMs. All of the partition are accessed each tRC clock cycle.
Memory can be accessed at same address across all memories. High bandwidth with 576b word.
Or, each partition can access any location in its partition independently of the access locations of the other partitions.
In effect, 4 fully random-access independent SRAMs. Still achieving a 576b wide data path.
MEMORY WORD WIDTH FOR DEEP AND WIDE MODES
DEEP MODE
- Single Port A
- Up to 288b
WIDE MODE
- Two Port A & B
- Port A
- Up to 288b
- Port B
- Up to 288b
- Combined Port A and Port B
- Up to 576b
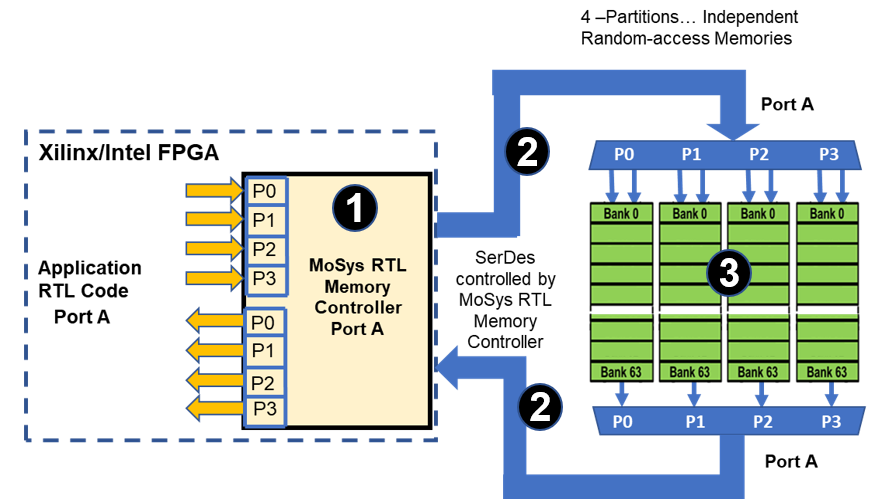
Total QPR Solutions has Three System Elements
MoSys defined the QPR memory as a solution product, with the goal of providing a simple path to upgrade designs from QDR with higher capacity but with a less design effort and minimal impact on software.
- MoSys supplied RTL Memory Controller
- QDR type RTL interface
- Provides RTL 72b registers
- Instruction/Data registers to memory
- Data registers from memory
- Support user selectable work widths
- Up to 576b
- Controls the SerDes protocol (transparent to user)
- SerDes high speed Memory/FPGA interface
- Most FPGAs have multiple SerDes lines
- QPR4 device available with 10 Gb/s or 12.5 Gb/s
- QPR8 devices available with 15 Gb/s or 25 Gb/s
- Lowest pin count interface…minimum of 8 FPGA pins
- Typical of 32 pins
- Preferred FPGA today and future interface direction
- QPR (Quad Partition Rate) memory Architecture
- Memory architecture with Partitions divided into Banks
- Each partition is accessed like an independent SRAM
- Bandwidth determined by user
MoSys RTL Memory Controller FPGA User Register Interface
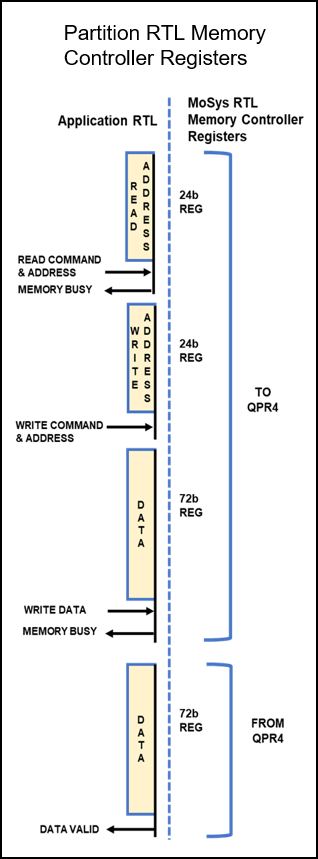
User Partition RLT interface set.
The MoSys Memory controller interface to the user is a simple set of registers. The QPR allows a Read, Write or a Read/Write to happen at the same time to a partition.
READ
The Read is a clocked 24b Address register.
WRITE
The Write registers are a 24b Address register and a 72b Data register both clocked at the same time.
READ/WRITE
The Read Address, Write Address and Write Data are all clocked into the registers at the same time. One rRC cycle
TOTAL READ/WRITES PER OPERATING MODE
DEEP MODE
- 4 READS
- 4 WRITES
- 4 READS & WRITES
WIDE MODE OPERATION
- 8 READS
- 8 WRITES
- 8 READ/WRITES

Memory Capacity
- From 576Mb to 1Gb
Costs
- 1/3 cost per Mbit
Design
- <10% of required QDR pins
- Faster board layout
- Less Power
Overall benefits
- Higher performance
- Higher memory capacity
- Easy to design
- Quicker time to market
QPR Family Comparison vs. QDR
- Memory size
- 4x to 8x common QDR
- Device PCB board space saving
- 1 device vs 4 or 8 QDR
- Signal pin reductions
- 4 QDRs: 500-720 pins
- 8 QDRs: 1072-1440
- 1 QPR4 OR QPR8: typical system 8 SERDES lanes
- All MoSys devices have Auto-Adaptation which handles on-board signal tuning, eliminating the need for any external components to ensure clean, reliable signals
- Cost
- One QPR4 with 4x the memory capacity is generally less than the price of 2 QDR memories
- One QPR8 with 8x the memory capacity is about 3 QDR memories
- Applications
- Larger buffers, High Bandwidth networking applications like search tables
- Allows real time operations and analysis at line or data rates
- Eliminates need for complex parallel
- operations using RLDRAM, HBM, or slow DRAM
Quazar Family Features/Benefits
- LOW COST
- 60-70% Less Costs than the equivalent QDR configuration
- Base Product: High Volume price of $175
- Provide high capacity
- 576Mb and 1Gb
- Fully random access to all memory locations
- Independent random-access partitions with simultaneous access
- Low tRC
- 2.6ns and 3.2ns
- Higher bandwidth
- 360 Gb/s
- Low power
- Less that half QDR
- MoSys RTL Controller with simplified QDR like register interface
- Equal or better performance than a QDR at a system level
- Up to 576 b word width
MoSys Applications Engines are available to discuss how MoSys QUAZAR QPR Memories or BLAZAR Bandwidth Engines can accelerate FPGA applications.
They are also experience in High Speed board design, layout and signal integrity as well as memory tradeoffs in FPGA designs regarding DRAM, FPGA SRAM and external SRAMs like MoSys high speed memories.
Contact Applications for details.
For pricing contact: MoSys Sales
