RMW Accelerator Engine ICs

Device Features
- 576 Mb memory with SerDes I/O
- Accessible through as few as 4 Lanes and as many as 16
- Deterministic Latency
- Embedded In Memory Functions
- Burst 2, 4 or 8 (EMIF)
- Two Separate Access Ports
- Full Production Qualified and Available
Superior, High Speed Random Access Memory Architecture
The heart of the memory IC is our advanced & parallel array of 1-T SRAM with a capacity of 576Mb.
- The memory is divided into 4 partitions allowing parallel (simultaneous) access. Each partition has 64 banks.
- There are two independent I/O ports per device, allowing for several memory access as well as multiple EIMFs to be executed in the same timeframe.
- Can be used as a Dual-Port memory
The tRC is 2.67 ns allowing up to 2.5 billion transactions per second.
Fixed In-Memory BURST Functions
The BURST Functions are focused on DATA MOVEMENT to accelerate getting data in and out of the memory faster and more efficiently by reducing the number of command cycles.
The BURST Read/Write In-Memory Functions can combine up to 8 READS and 8 WRITES into a single BURST command. This reduces the number of command cycles when moving data, nearly tripling the amount of data that can be moved in the same timeframe.
The Accelerator Engine can do several BURST Functions simultaneously, further increasing system performance.
High-Speed Serial Protocol I/O Interface
MoSys’s Accelerator Engines are designed using 16 SerDes lanes that can transmit data up to 12.5Gbps, with an optional rate of 10Gbps. MoSys’ GigaChip Interface (GCI) delivers full duplex, CRC protected data throughput, enabling up to 2.5 billion memory transaction per second on as few as 16 SerDes Lanes.
Traditional memory design requires many more interface pins (in some cases 1000s of pins), making signal routing and integrity a design challenge.
Each Accelerator Engine has 2 independent, 8 lane, I/O ports that allow simultaneous memory access operations.
Fixed In-Memory RMW Functions
The RMW Functions are focused on DATA COMPUTING where there is need for memory location modification involving RMW in applications such as metering, as well a single or Dual Counter update for statistics.
Traditional memory location modification requires one command to READ a memory location, a second operation to MODIFY the value, and a third command to WRITE the new value back to the memory location.
The RMW Functions provide a least two levels of acceleration. First, the RMW functions can be executed with a single command. Second, since the modification is executed within memory, there is no need to move the data out to be modified, and then back into memory to write. This removes all of the associated I/O latency.
Easy to Design-In
- Fewer pins using serial I/O with the GigaChip Interface technology
- Clean and reliable signal integrity board layout
- Standard replacement for QDR
- Simple to understand EIMF (Embedded In-Memory Functions) to accelerate performance
- High speed random access memory, with easy to understand EIMFs, with so fewer signal pins
- Architected to allow for a straight-forward design-in process
Bandwidth Engine 2 – RMW Architecture
Understanding MoSys’ Advanced 1T-SRAM Technology
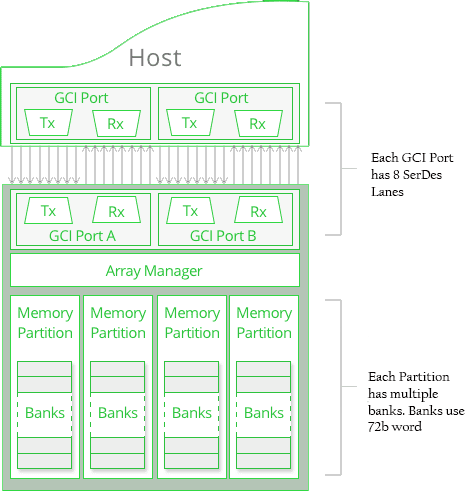
Parallel Array Architecture
- 16 outstanding transactions
- 3.75 Billion Transactions per Second (2.5B Reads & 1.25B Writes)
- 160Gbps full duplex throughput
- 16ns deterministic read latency
- 2.67ns Random Cycle time (tRC)
GigaChip Interface
- 90% efficient throughput
- Up to 16 low-latency SerDes lanes (10.3125Gbps or 12.5Gbps)
Single-Cell SRAM 70x better SER
- Full ECC support
- CRC protected and self-recovering
- SEU resistant
BE2-BURST Throughput Increase
BURST Fixed-Functions
Burst functions are designed to get data in and out of the memory more efficiently by reducing the number of commands. Normal transmission requires one command for each transfer of data. However, by bundling eight data words to a single command, designers can eliminate seven unnecessary commands. The BURST commands enable the transmission of 2, 4 or 8 words* per command cycle.
* word = 72 bits
| SerDes Speed Grade | |||
| 10.3125Gbps | 12.5Gbps | ||
| Width | BURST | Throughput (Gbps) | Throughput (Gbps) |
| 16 Lanes | BL8 | 132 | 160 |
| BL4 | 118.8 | 144 | |
| BL2 | 99 | 120 | |
| 8 Lanes | BL8 | 66 | 80 |
| BL4 | 59.4 | 72 | |
| BL2 | 49.5 | 60 | |
| 4 Lanes | BL8 | 33 | 40 |
| BL4 | 29.7 | 36 | |
| BL2 | 24.8 | 30 | |
BE2-RMW Embedded In-Memory Function Overview
ALU/Logical on 72b
- add, sub, adc, sbb, s1add, s2add, s3add, s3sub, and, or, xor, andn, sar, sir, sll, minu, maxu, mult
Atomic Operations
- Local:
- 8b, 16b, 32b and 64b
- adda, suba, anda, xora, andna, xchga, cmpxchga
- Partition
- 16b, 32b, and 64b
- Add(s), sub(s), xor, rd/set, tst/set, cmp/set, avg, tm, age
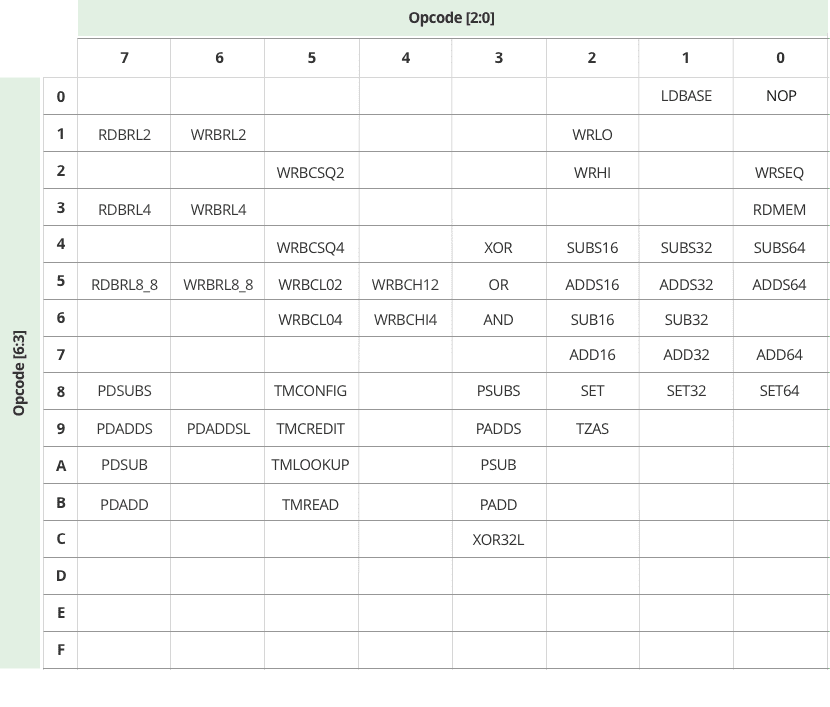
BE2-RMW Embedded In-Memory BURST and RMW Function Opcode Map